Green Hydrogen
With ProMax 6.0, BR&E introduces new process blocks for simulating water electrolysis to produce Green Hydrogen:
- Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM)
- Alkaline Water Electrolysis (AWE)
- Solid Oxide Electrolysis (SOE)
Many alternate combinations of properties available for solving the electrolyzer including:
- Total Power Input
- Hydrogen Production Target
- Fraction Inlet H2O Conversion
- Current Density
- Area per Cell
- Cells per Stack
- Stacks per Facility
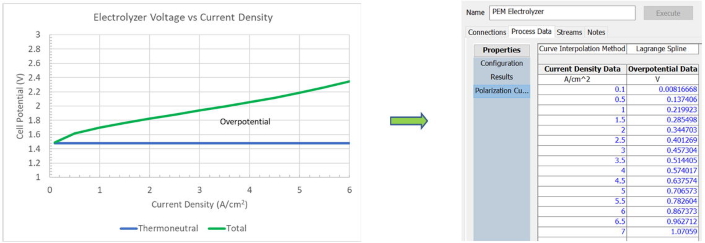
Electrolyzer performance is characterized by:
- Reversible Cell Voltage from ProMax’ thermodynamic properties
- Overpotential Voltage by
- User-specified constant value
- Voltage vs Current Density curve entry
Product Impurities are predicted or specified:
- Hydrogen Crossover
-
- Ulleberg correlation when using AWE
- H2 and O2 Conversion to Water with SOE
- Oxygen Crossover
- H2 and O2 Conversion to Water with SOE
- Water Crossover
- Electro-Osmotic Drag Coefficient when using PEM
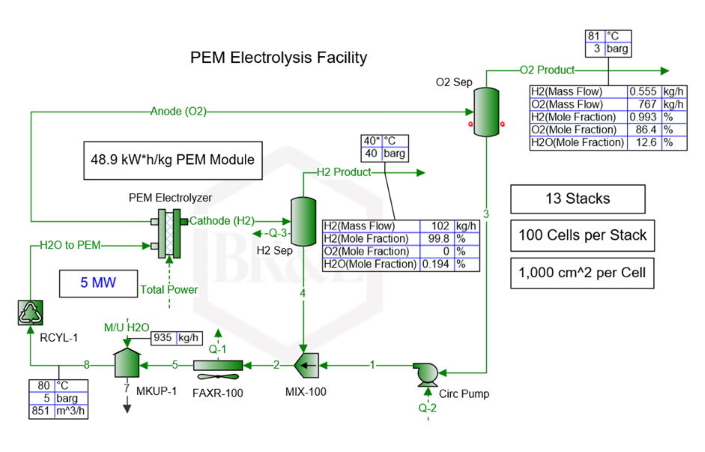
Reported properties on Cell, Stack, and Facility basis include:
- Reversible, Overpotential, and Total Voltage
- Current
- Power
- Hydrogen Yield
- Efficiencies
Separate Pressure Changes for Anode and Cathode Sides